ICMS Approach to Cloud Security
ICMS leverages cloud technologies for our infrastructure and focusses maintaining the highest level of security to protect our consumers’ data and earn their trust.
This security framework is based on the following principles:
- Multiple layers of security across the entire cloud infrastructure.
- Encryption of data both in transit and at rest to ensure data security throughout the entire data lifecycle.
- Native cloud-based security tools to monitor for potential threats and vulnerabilities.
- Third party providers to augment security assessments and threat detection.
Why Cloud Security Is Important?
Many businesses have quickly deployed cloud-based solutions over the past two years to allow for more flexible working arrangements. The migration of data, infrastructure, and apps from an on-premises setup to the cloud helps hybrid workers be more productive.
Access to more tools, improved data availability, optimized team collaboration, and simpler content management are just some of the benefits of moving to the cloud. However, security issues may keep some organizations from making the leap. This is where cloud-based security comes into play.
Cloud security, also referred to as cloud computing security, is a combination of processes and tools aimed to manage both external and internal risks to the security of a company’s information technology infrastructure. Secure cloud computing is becoming increasingly important as companies progress along the path of digital transformation and adopt cloud-based applications and services into their architecture.
These security protocols are designed to safeguard cloud data, meet regulatory requirements, and preserve customers’ privacy. Security in cloud computing can be tailored to meet the specific needs of a company, from authenticating users to screening traffic. Furthermore, since these standards can be set up and monitored from a single point, administrative costs are minimized, allowing IT teams to devote more time to other aspects of the business.
Types of Cloud Environments
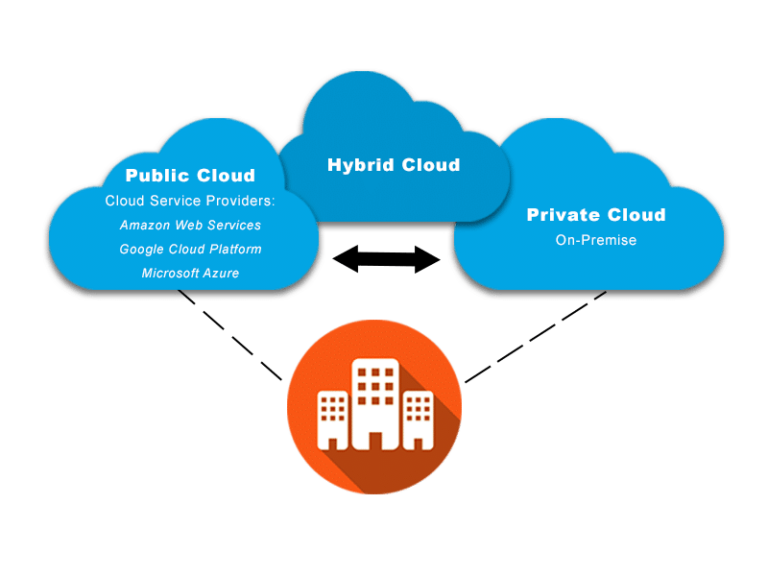
There are three primary types of cloud environments to consider in cloud-based security. It’s critical to understand the differences between these three since they each present unique challenges and opportunities in terms of security.
Private cloud: A private cloud is typically used for internal computing within a single company. As such, it is incompatible with transactions and collaboration with other institutions.
Public cloud: Unlike the private cloud, which is managed by the company itself, a public cloud is run by a third party. In most cases, it’s used by multiple organizations.
Hybrid cloud system: As its name implies, the hybrid cloud is an efficient combination of both public and private cloud environments. With hybrid systems, you can benefit from the scalability offered by public clouds while also maintaining better control over your resources like a private cloud.
Benefits of Cloud Security

Cloud computing’s now well-acknowledged advantages can only be realized with an effective cloud security system. Here are some securities of the cloud benefits:
Reduced initial outlay: With cloud computing, you don’t have to worry about purchasing expensive on-premises hardware.
Lower operating and administrative costs: Using a Cloud Service Provider eliminates the need to spend money on in-house security professionals to perform manual upgrades and setups.
Scalability: By using the cloud, you can easily expand your data and application storage capacity as your needs change.
Improved availability and reliability: Cloud security ensures that authorized users can readily access your data and apps. You’ll always have access to your cloud apps and data, allowing you to address any possible security concerns swiftly.
Centralized security: Cloud computing security protects your apps, devices, and data by centralizing management.
The Bottomline
As we shift more and more of our data, devices, business operations, and other functions to the cloud, cloud security grows increasingly crucial. With the prevalence of cyber-attacks and data leaks, organizations must prioritize the protection of their IT infrastructure. As such, it is vital to collaborate with a cloud service that provides excellent security tailored to your specific architecture.

